It is difficult to achieve optimal performance of your data center and networks, especially in a virtualized environment. Fortunately, effective implementation of 40/100 Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) can help pave the way for a fully functional virtualized network.
In the following guide it explores the benefits of 40/100 GbE implementation in a virtualized environment and how it can maximize existing infrastructure investments.
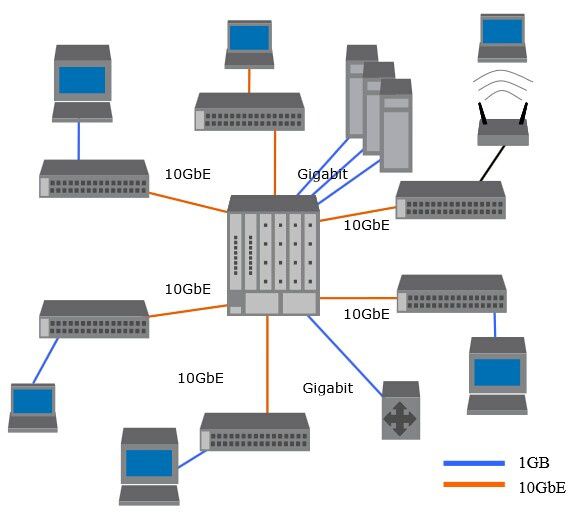
40/100GbE is rapidly gaining traction as a key foundation for building the next generation of virtualized data center and campus environments. The 40/100GbE-based architecture for virtualized data center and campus is illustrated in the paper. IT managers are increasingly aware of the benefits and advantages1 offered by 40/100GbE as well as its promise as an interconnect option among data centers and commercial buildings in the campus.
On the economic side, barriers to entry in the 40/100GbE space continue to fall. Capital investment in 10GbE networks today can be protected when upgrading to 40/100GbE networks in the future. The Ethernet switching and fiber cabling examples in this paper illustrate:
• 55 percent2 of on switching equipment can be protected
• 57 percent3 of investment on fiber cabling can be preserved
On the availability side, more vendors have supplied solutions for the 40/100GbE ecosystem, and a number of multi-vendor interoperability events on 40/100GbE technology have been hosted by the Ethernet Alliance? With both Cisco? and CommScope? Actively participating. So, early adoption anxieties over locked-in vendor relationships have evaporated. The greater availability from multiple vendors and declining deployment costs due to broader adoption in the marketplace make 40/100GbE infrastructure a sound and prudent investment, both for today and tomorrow.
The increased traction of 40/100GbE has led to its best practice status as the standard for the next generation of high-bandwidth virtualized applications. This adoption has been fueled by both its superior performance and economic benefits in virtualized environments.
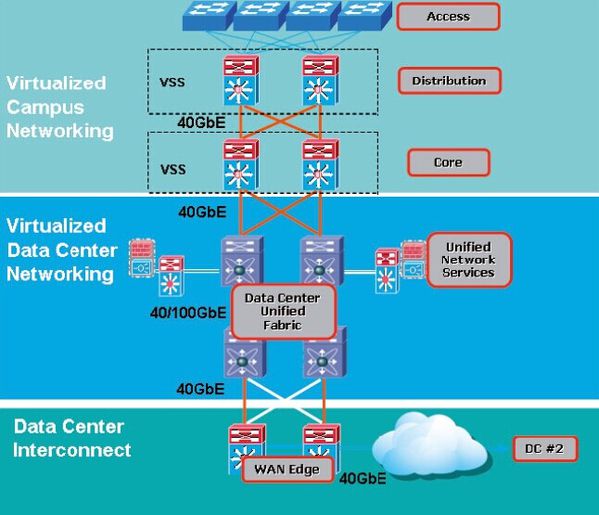
40/100GbE based architecture for virtualized Data Center and campus
![40-100GbE-based-architecture-for-virtualized-Data-Center-.jpg]()
Virtualized Data Center
True data center virtualization is end-to-end virtualization, including server virtualization, storage virtualization, and network virtualization, and can result in many diverse benefits. Virtual machines and networks can be quickly and nimbly deployed. Their energy efficiency and capacity can dynamically scale to meet the demands of variable workloads without wasting resources. Disaster recovery is faster, and both initial and ongoing costs can be lower than those of traditional non-virtualized approaches.
In the journey to the virtualized data center and cloud, data center managers face a number of design and operational challenges. One of the most conspicuous challenges for network design is to provide enough bandwidth for the applications of today and the foreseeable future. With converged network technologies, 10GbE, which is becoming a de facto choice for server access networks, can be a good choice for a storage access network as well. Given 10GbE at the access layer, 40/100GbE is recommended for aggregation and core layers of networks in data centers, and this is where 40/100GbE removes the constraints that have previously prevented virtualized data centers from fulfilling their maximum potential.
Virtualized Campus
Video is a strongly growing application in campus networks. Video applications are more than just video conferencing or video streaming. Enterprise video applications include desktop high definition video, video phone, enterprise TV, IP video surveillance and other video generation and sharing. Bring your own device (BYOD) is another emerging trend in the campus network. Video, voice, data and BYOD put pressure on a campus’s distribution and core networks.
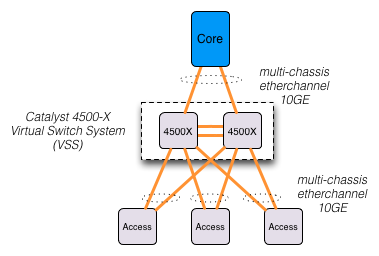
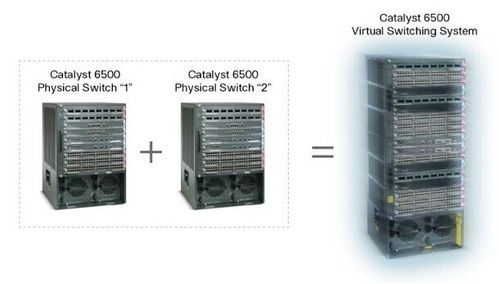
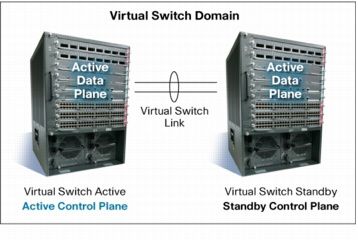
Compared to traditional layer 2 and 3 network design in the campus, the core and distribution networks can be virtualized by using Virtual Switching System (VSS) with Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switches. VSS is a network system virtualization technology that pools two or more Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches into a virtual one. A VSS scales system bandwidth capacity with automatic load sharing. A VSS increases operational efficiency by simplifying the network and reducing switch management overhead by at least 50 percent. A VSS boosts nonstop communications with no disruption to applications. A VSS enhances existing multilayer switching architecture without fundamentally changing the architecture, resulting in ease of adoption and migration of the technology.
Ecosystem
A list of examples of 40/100GbE Ethernet switching and cabling solutions from Cisco and CommScope.
40/100GbE ecosystem examples
![40-100GbE-Ecosystem-Examples.jpg]()
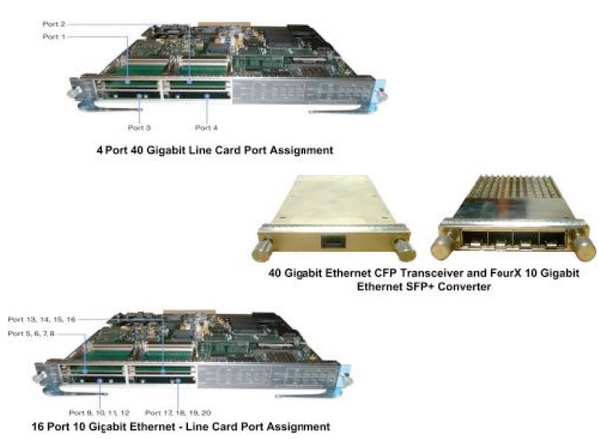
The new Cisco Catalyst 6900 Series 4-Port 40GbE Fiber Module (WS-X6904-40G) for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches was developed for deployment in the enterprise campus distribution layer and core layer, in traditional data centers with 10 Gigabit aggregation, and in metro-Ethernet-based data center interconnections, as well as in multipurpose service provider networks, which require high-performance data throughput coupled with security, manageability, virtualization, and quality of service.
The WS-X6904-40G module supports 10GbE and 40GbE interfaces. Figure 2 shows the 10GbE and 40GbE interfaces of Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switches. This new module is the only solution that supports both connections in a single format, for flexible migration. There are also many other new and exciting capabilities unique to the WS X6904-40G module, such as CTS (Cisco Trust Sec) for end-to-end role-based security deployment using SGT (Security Group Tagging) and SGACL (Security Group Access Control List) and link-by-link encryption based on IEEE 802.1AE MACsec (MAC based Security) standard, VNTag (Virtual Network Tag), and extensive quality of services features. The 40GbE Fiber Module is a perfect choice for forming a campus core network by interconnecting the physical switches of a VSS in core/distribution layer networks in the campus. It also can be utilized to connect access switches to a VSS at the distribution layer of the campus network. Users are deploying this module today and using it for four 10GbE links until they really need a true 40GbE channel.
Cisco Catalyst 10GbE and 40GbE Fiber Modules and optical transceivers
![10GbE-and-40GbE-interfaces-of-Cisco-Catalyst-6500-series-sw.png]()
CommScope SYSTIMAX? InstaPATCH? 360 Pre-Terminated Fiber Solutions enable network operations in the data center at the current 10GbE speed of today, while provisioning for eventual upgrades to 40GbE and/or 100GbE. These solutions were tested, qualified and demonstrated in multi-vendor closed-door and open-to-public environments at both transceiver and system levels.4 Results repeatedly demonstrated that the performance of InstaPATCH 360 Pre-Terminated Fiber Solutions and LazrSPEED? Multimode fiber solutions far exceed the cable reach specified in IEEE Std. 802.3baTM-2010, “40 and 100 Gigabit Ethernet” standards.
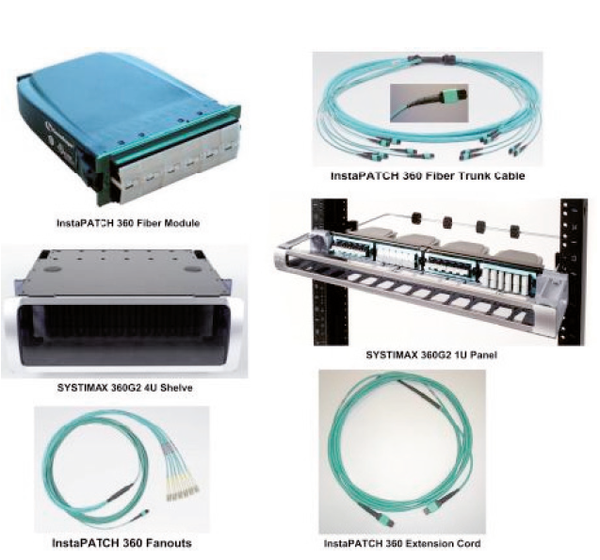
SYSTIMAX InstaPATCH 360 Pre-Terminated Fiber Solutions utilize the standard Method B polarity scheme. Customers who have chosen the fiber solution have invested in high-performance and high-quality fiber solutions, but also have purchased peace of mind: their data center fiber cabling infrastructure is ready for 40/100GbE whenever and wherever they need it. The eventual upgrade can be a simple and painless process. Figure 3 shows samples of SYSTIMAX InstaPATCH 360 Pre-Terminated Fiber Solutions.
Samples of SYSTIMAX InstaPATCH 360 Pre-Terminated Fiber Solution
![Samples-of-SYSTIMAX-InstaPATCH-360-Pre-Terminated-Fiber-Sol.png]()
Solutions Designed to Maximize Return on Investment
The switching solutions from Cisco and cabling solutions from CommScope enable easy adoption of 10GbE today and seamless upgrades to 40/100GbE in the future.
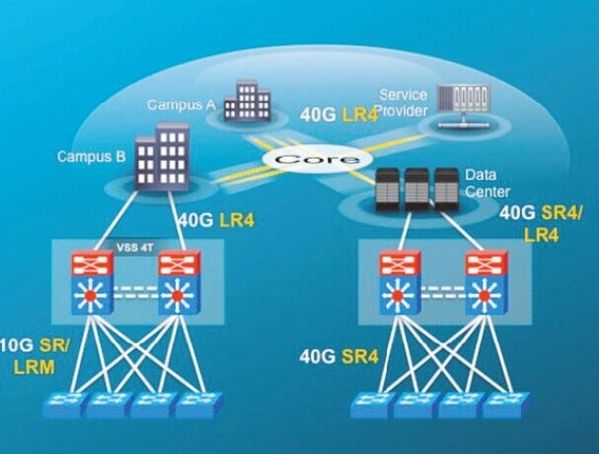
The Cisco Catalyst 6500 E-Series chassis, 6900 series 10GbE and 40GbE modules, and Supervisor T2 module provide the easy upgrades. End users’ investment protection can be achieved by redeploying the common components. The common switching components may include a Catalyst 6500 E-Series chassis, a supervisor module Sup2T, and two power supplies. As illustrated in the example in Figure 4, end users can save 55 percent1 of capital expense on the common components for 40GbE short reach (SR), or 47 percent1 of expenses for 40GbE long reach (LR) when upgrading from 10GbE.
40GbE deployment in campus
![40GbE-deployment-in-campus.jpg]()
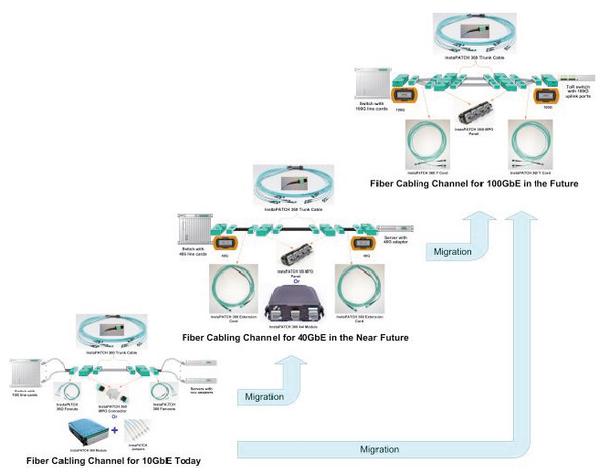
Similarly, CommScope SYSTIMAX InstaPATCH 360 Pre-Terminated Fiber Solutions offer seamless migration from 10GbE to 40/100GbE with investment preservation. A typical preterminated multimode fiber cabling channel is composed of components such as apparatus, patch cord, patch panel or shelf, and Multi-Fiber Push On (MPO) trunk cable. Figure 5 illustrates the fiber cabling channel for 10, 40 and 10 Gigabit Ethernet link, respectively. It’s noticeable that the common cabling component among the three channels in Figure 5 is the pre-terminated fiber trunk cable. Figure 5 also provides a cabling infrastructure migration path from 10GbE today to 40 or 100GbE in the future.
Fiber cabling migrations from 10GbE to 40/100GbE
![Fiber-cabling-migrations-from-10GbE-to-40-100GbE.png]()
Each physical Ethernet link has one cabling channel. The cabling cost of four 10GbE links (or channels), one 40GbE link, ten 10GbE links and one 100GbE. The cost is the result of adding the costs of all the cabling components and then dividing the sum by the number of Ethernet links (or cabling channels) for each corresponding speed.
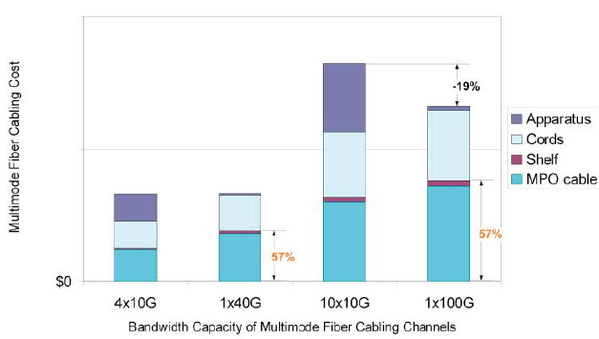
The investment preservation example5 on pre-terminated fiber cabling
![The-investment-preservation-example5-on-pre-terminated-fibe.png]()
With the reuse of the common cabling components—which are the SYSTIMAX InstaPATCH 360 Trunk Cable and 360G2-1U Modular Shelf in this example—end users can save 57 percent2 of the capital expense on multimode fiber cabling when migrating from today’s 10GbE to either 40GbE or 100GbE in the future.
The costs for 4x10G and 10x10G fiber cabling are denoted in Figure 6 for a rough reference to their corresponding counterparts of 40 and 100GbE, respectively. The fiber cabling cost for 1x40G is close to the one for 4x10G, while the 1x100G cost is 19 percent less than the one for 10x10G’s cost, in this example.
You may be wondering why the cost of the MPO cable increases when migrating from 4x10G to 1x40G and from 10x10G to 1x100G. This is because, as there are unused fibers, only a fraction of the trunk cost is allocated to the 10GbE scenarios; but for the 40G and 100G scenarios, the total trunk cost is allocated. In other words, only four out of six possible fiber circuits are lit in the 4x10G case, so only 4/6ths of the cost is applied. Similarly, only 10 out of 12 possible fiber circuits are lit in the 10x10G case so only 10/12ths of the cost is applied. Notice that the 57 percent investment preservation on fiber is not the only saving for end users.
When the distribution and core layer networks migrate to 40/100GbE, the apparatus and cords can be reused in other parts of the networks: for example, the access layer network for 10GbE or even Fibre Channel SAN networks. By doing so, end users may preserve more of their investment.
The ongoing adoption of 40/100GbE is already redefining the IT landscape. It represents the first step toward the next generation of high-bandwidth connectivity demanded by virtualized data centers and campuses. As 40/100GbE continues to unlock the full performance and economic potential of virtualized environments and more campus deployments, it will undoubtedly solidify its position as the new standard for best practice, speed and reliability.
Because it affords instant benefits as well as a streamlined upgrade path, forward-looking IT managers would be well advised to include 40/100GbE as a key part of any upgrade or new deployment plans, particularly those that include a need for campus-wide interconnectivity between data centers, and inside data centers and office buildings. In particular, Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switches with their 40GbE fiber module and CommScope SYSTIMAX InstaPATCH 360 pre-terminated, LazrSPEED and TeraSPEED? fiber solutions deliver the performance and reliability that position today’ s investment for rich returns in the future.
References and Notes
1. G. Chanda from Cisco and Y. Yang from CommScope, “40 GbE: What, Why & Its Market Potential”, Ethernet Alliance white paper, November, 2010
2. The two percentages can vary based on a number of factors, such as hardware configurations, purchasing prices, etc. The new installation must be tested and meet the specifications issued by Cisco Systems.
3. The percentage can vary based on a number of factors, such as MPO trunk cable length, cabling channel configurations, purchasing prices, etc. The new installation must be tested and meet the specifications issued by CommScope SYSTIMAX.
4. D. Hall and Y. Yang from CommScope, “40/100 Gigabit Ethernet Eco-System is Alive and Well”, CommScope white paper, 2011
5. In the example of Figure 6, the MPO trunk cable length is 174 feet and the cord length is 10 feet. These lengths are determined based on Paul Kolesar’s contribution to IEEE 802.3 Next Gen 40G and 100G Optics Study Group in May 2012, “Cabling Cost-Centroid Lengths for Simplified Total Cost Comparisons”.
The multimode fiber cabling channel configuration for the example in Figure 6 is an interconnect configuration. In the 10GbE cabling channels, two fiber modules are connected back to back by MPO trunk cables, and LC jumpers are plugged in to connect the fiber modules at both ends. In the 40/100GbE cabling channels, two MPO adapter panels are connected back to back by an MPO trunk cable, and equipment cords are plugged into MPO adapter panels at both ends.
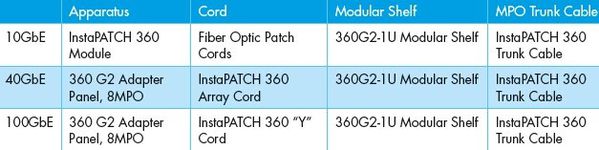
The following table lists the products used in the cost study for the investment preservation example5 on pre-terminated fiber cabling
![the-products-used-in-the-cost-study-for-the-investm-copy-1.jpg]()
More Network Topics
Cisco Intercloud Fabric for Providers & Business
What are the Considerations While Buying a Cisco Next-Generation Firewall?
Selecting Cisco Switches, For Campus or Branch?
10GBASE-T or SFP Plus